

Structure and patterns |
← |
Bamboo flooring has three structures: horizontal, vertical and processed fiber (array).
Horizontal bamboo flooring
The horizontal bamboo floor structure, also known as "plain squeezing" or "flat pressing", is obtained by pressing the bamboo strips in three layers of their planes. During production, bamboo strips are pressed together in the same direction, in parallel with the three layers. The distinctive feature of the horizontal structure of the bamboo floor is that they have a traditional "joint" pattern that repeats itself throughout the length of the table.

Vertical bamboo flooring
The vertical bamboo floor structure, otherwise known as "side squeezing", is obtained by pressing the bamboo strips on its side. Unlike the horizontal structure, the strips are pressed with only one layer. During production, the bamboo strips are arranged vertically adjacent to each other, glued together and tightly pressed. The distinctness of the bamboo floor structure is that, unlike the horizontal structure, the visibility of the joints is significantly reduced, resulting in a cleaner and even surface of the boards with a long, linear hardwood appearance.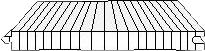
Bamboo flooring of treated bundle
Bamboo flooring, otherwise known as "pressed press", is made by compressing bamboo strips in high pressure environments using heat-sensitive, low-volatile organic adhesives. Bamboo stems are cut along the length, split into individual joists and loaded with cold presses at a load of 2500 tons. After the hardening process, the squeezed block is cut to the floor slabs, which completes the chosen decoration and laying structure accordingly. The bamboo flooring of the treated bamboo is a contemporary performance and a hardwood floor covering that exceeds the hardness of even the finest tropical hardwood floors.
| ↑ | ← |